SensoMod
Holistic conceptual Design of Sensor Modules for Machine Elements
Method Development for the Integration of Sensor Functions into Mechatronic Systems
Initial situation
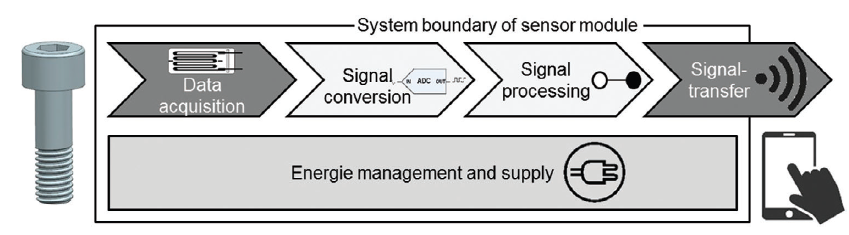
The increasing digitalization in mechanical engineering calls for novel concepts for acquiring and processing process data. Sensor-integrated machine elements (SMEs) offer a way to capture technical states in situ and contribute to the implementation of cyber-physical systems. In this context, not only the sensor principle itself is relevant, but also additional functions such as signal conversion, conditioning, transmission, and energy supply. However, holistic methodological approaches for the development of highly integrated sensor modules that systematically consider these functions are still lacking. Therefore, a methodological framework for the design of sensor modules for machine elements is researched, based on insights from mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and information technology.

Project objectives
The objective of this project, funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), is to develop methodological support for the holistic design of sensor modules for machine elements. In this context, “holistic” refers both to the consideration of all sensor subfunctions and to all phases of the product life cycle. The focus lies on selecting solution principles for the individual subfunctions, integrating them into comprehensive module combinations, and evaluating these combinations with respect to robust operating strategies and minimal energy requirements. By exchanging knowledge with projects of the Priority Program SPP 2305 and analyzing their approaches, the project aims to contribute to the theoretical foundation of method-based development of sensor-integrated machine elements and thereby accelerate digitalization.
Approach
The project is structured into five interrelated work packages. First, the relevant sensor subfunctions of the intended system are identified and analyzed. For each subfunction, possible solution principles are modeled and systematically categorized to create a comprehensive and structured foundation for later module combinations. Based on this, a methodological framework is developed for selecting and integrating suitable principles, taking into account both functional and physical dependencies. A further focus lies in investigating system robustness: relevant disturbance factors are identified and quantitatively assessed with respect to their impact on the sensor modules and their subfunctions. Finally, strategies for the energy-efficient operation of components within the system context are developed. The theoretical methodology will be verified and validated by implementing a prototype user tool.



